PyTorch GPU inference with Docker and Flask

GPU inference In a previous article, I illustrated how to serve a PyTorch model in a serverless manner on AWS lambda. However, currently AWS lambda and other serverless compute functions usually run on the CPU. But what if you need to serve your machine learning model on the GPU during your inference and the CPU just doesn’t cut it?
In this article, I will show you how to use Docker to serve your PyTorch model for GPU inference and also provide it as a REST API.
PyTorch Model in Production as a Serverless REST API
PyTorch is great to quickly prototype your ideas and get up and running with deep learning. Since it is very pythonic, you can simply debug it in PyCharm as you are used to in regular Python.
However, when it comes to serving your model in production the question arises: how to do it?
There are many possibilities to do so, but in this post, you will learn how to serve it as a lambda function in a serverless manner on AWS.
Deep Learning on Medical Images With U-Net
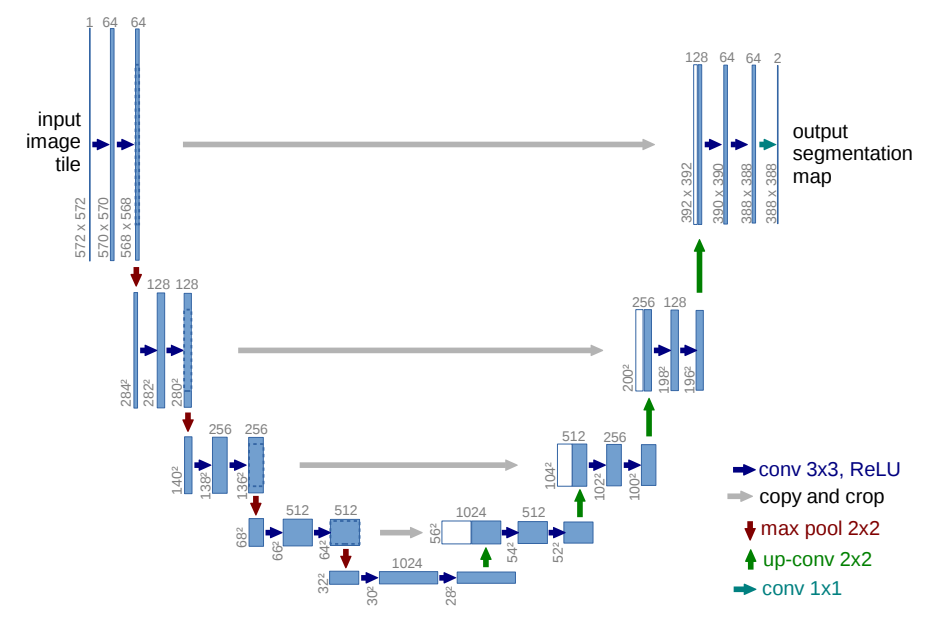
Illustration taken from the U-Net paper
I recently read an interesting paper titled “U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation” by Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox which describes how to handle challenges in image segmentation in biomedical settings which I summarize in this blog post.
Challenges for medical image segmentation A typical task when confronted with medical images is segmentation. That refers to finding out interesting objects in an image.
Play Video Games Using Neural Networks
Deep Q Learning Today, I want to show you how you can use deep Q learning to let an agent learn how to play a game. Deep Q learning is a method which was introduced by DeepMind in their 2015 Nature paper (pdf) to play Atari video games by just observing the pixels of the game. To make it a bit simpler for the case of this blog post, we will use a slightly easier game which is to balance a polestick on a paddle.