Graphical Explanation of Neural Networks and Gradients with Python
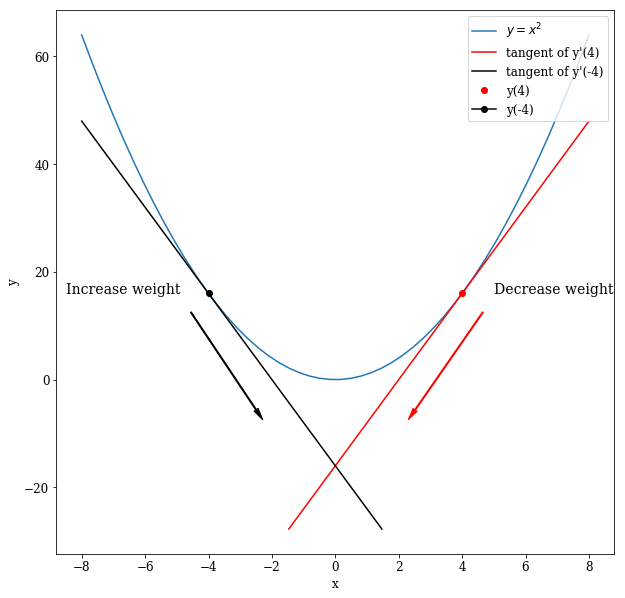
How does an artificial neuron work? Inspired by neurons of the human brain, an artificial neuron receives several input values.
These input values are multiplied with the weights of the neuron which reflects that some input values are activating the neuron (positive weights) while others inhibit the neuron (negative weights).
The product values are then summed and together create the activity a.
Finally, a non-linear function is applied on a to yield the final output of the neuron.
Debugging Tensorflow
Debugging Tensorflow Today, I am going to explore different ways to debug Tensorflow which can be a bit cumbersome at times. However, there are a few good possibilities that I know of to get more insight into the inner workings of Tensorflow.
It’s a little more complicated than regular debugging like say in PyTorch where you can use an IDE like PyCharm and simply set breakpoints in your code to stop and inspect what’s going on.
Deep Learning on Medical Images With U-Net
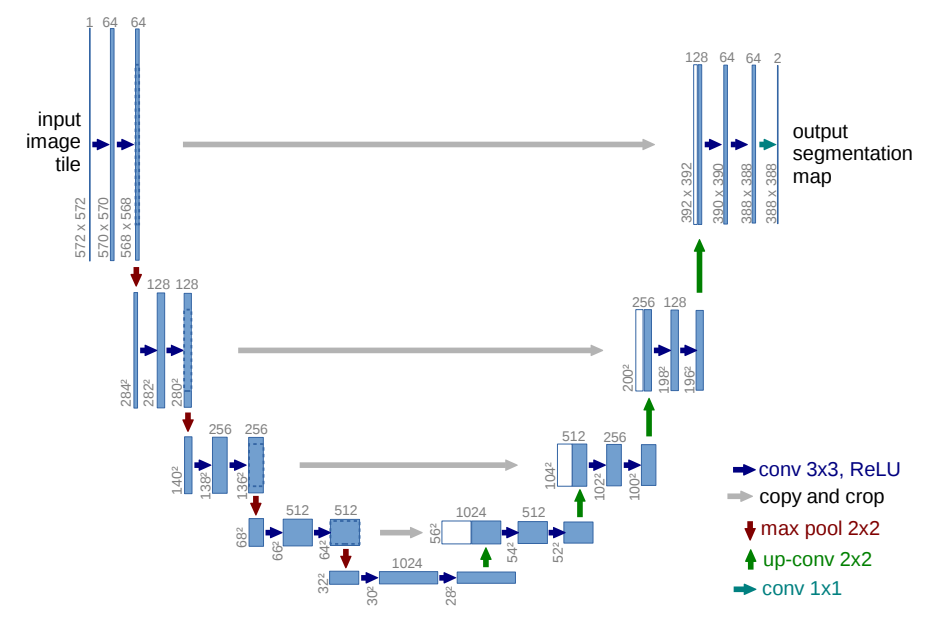
Illustration taken from the U-Net paper
I recently read an interesting paper titled “U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation” by Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox which describes how to handle challenges in image segmentation in biomedical settings which I summarize in this blog post.
Challenges for medical image segmentation A typical task when confronted with medical images is segmentation. That refers to finding out interesting objects in an image.
Play Video Games Using Neural Networks
Deep Q Learning Today, I want to show you how you can use deep Q learning to let an agent learn how to play a game. Deep Q learning is a method which was introduced by DeepMind in their 2015 Nature paper (pdf) to play Atari video games by just observing the pixels of the game. To make it a bit simpler for the case of this blog post, we will use a slightly easier game which is to balance a polestick on a paddle.